Here is my plan for John Zogg’s battery charger. It uses 3 analog inputs for each battery cell. I decided to use this one that
/*
* UnoCharge - the arduino nimh charger
* This is my version of the Arduino NiMh battery charger
* its modifications include Charge LED and multiple Battery support
* Orginally from https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/projects/create-an-arduino-controlled-battery-charger/
* Modified by delphijustin
* Special Thanks to John Zogg and flyback
*/
byte nBatteries=2;//Number of batteries(1 through 5), other array variables must have the same number of values.
byte chargedLED = 2; // digital pin for LED
int batteryCapacity[] = {2500,2500}; //capacity rating of battery in mAh
float resistance[] = {10.0,10.0}; //measured resistance[b] of the power resistor
int cutoffVoltage = 1600; //maximum battery voltage (in mV) that should not be exceeded
float cutofftemperatureC = 35; //maximum battery temperature that should not be exceeded (in degrees C)
//float cutoffTemperatureF = 95; //maximum battery temperature that should not be exceeded (in degrees F)
long cutoffTime = 46800000; //maximum charge time of 13 hours that should not be exceeded
byte outputPin[] = {9,6}; // Output signal wire connected to digital pin 9
int outputValue[] = {150,150}; //value of PWM output signal
byte analogPinOne[] = {0,3}; //first voltage probe connected to analog pin 1
float ValueProbeOne[] = {0,0}; //variable to store the value of analogPinOne[b]
float voltageProbeOne[] = {0,0}; //calculated voltage at analogPinOne[b]
byte analogPinTwo[] = {1,4}; //second voltage probe connected to analog pin 2
float valueProbeTwo[] = {0,0}; //variable to store the value of analogPinTwo[b]
float voltageProbeTwo[] = {0,0}; //calculated voltage at analogPinTwo[b]
byte analogPinThree[] = {2,5}; //third voltage probe connected to analog pin 2
float valueProbeThree[] = {0,0}; //variable to store the value of analogPinThree[b]
float tmp36voltage[] = {0,0}; //calculated voltage at analogPinThree[b]
float temperatureC[] = {0,0}; //calculated temperature of probe in degrees C
//float temperatureF = 0; //calculated temperature of probe in degrees F
float voltageDifference[] = {0,0}; //difference in voltage between analogPinOne[b] and analogPinTwo[b]
float batteryVoltage[] ={0,0}; //calculated voltage of battery
float current[] = {0,0}; //calculated current through the load (in mA)
float targetCurrent[] = {0,0}; //target output current (in mA) set at C/10 or 1/10 of the battery capacity per hour
float currentError[] = {0,0}; //difference between target current and actual current (in mA)
void setup()
{
pinMode(chargedLED,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(chargedLED,LOW);
Serial.begin(9600); // setup serial
for(byte x=0;x<nBatteries;x++){
targetCurrent[x]=batteryCapacity[x]/10;
pinMode(outputPin[x], OUTPUT); // sets the pin as output
}
}
byte chargeStatus(){
byte s=0;
for(byte b=0;b<nBatteries;b++){
if(outputValue[b]==0){s++;}
}
if(s==nBatteries){
digitalWrite(chargedLED,HIGH);
}
return s;
}
void loop()
{
for(byte b=0;b<nBatteries;b++){
Serial.println("Battery "+b);
analogWrite(outputPin[b], outputValue[b]); //Write output value to output pin
Serial.print("Output: "); //display output values for monitoring with a computer
Serial.println(outputValue[b]);
ValueProbeOne[b] = analogRead(analogPinOne[b]); // read the input value at probe one
voltageProbeOne[b] = (ValueProbeOne[b]*5000)/1023; //calculate voltage at probe one in milliVolts
Serial.print("Voltage Probe One (mV): "); //display voltage at probe one
Serial.println(voltageProbeOne[b]);
valueProbeTwo[b] = analogRead(analogPinTwo[b]); // read the input value at probe two
voltageProbeTwo[b] = (valueProbeTwo[b]*5000)/1023; //calculate voltage at probe two in milliVolts
Serial.print("Voltage Probe Two (mV): "); //display voltage at probe two
Serial.println(voltageProbeTwo[b]);
batteryVoltage[b] = 5000 - voltageProbeTwo[b]; //calculate battery voltage
Serial.print("Battery Voltage (mV): "); //display battery voltage
Serial.println(batteryVoltage[b]);
current[b] = (voltageProbeTwo[b] - voltageProbeOne[b]) / resistance[b]; //calculate charge current[b]
Serial.print("Target Current (mA): "); //display target current[b]
Serial.println(targetCurrent[b]);
Serial.print("Battery Current (mA): "); //display actual current[b]
Serial.println(current[b]);
currentError[b] = targetCurrent[b] - current[b]; //difference between target current[b] and measured current[b]
Serial.print("Current Error (mA): "); //display current[b] error
Serial.println(currentError[b]);
valueProbeThree[b] = analogRead(analogPinThree[b]); // read the input value at probe three
tmp36voltage[b] = valueProbeThree[b] * 5.0; // converting that reading to voltage
tmp36voltage[b] /= 1024.0;
temperatureC[b] = (tmp36voltage[b] - 0.5) * 100 ; //converting from 10 mv per degree wit 500 mV offset to degrees ((voltage - 500mV) times 100)
Serial.print("Temperature (degrees C) "); //display the temperature in degrees C
Serial.println(temperatureC[b]);
/*
temperatureF = (temperatureC[b] * 9.0 / 5.0) + 32.0; //convert to Fahrenheit
Serial.print("Temperature (degrees F) ");
Serial.println(temperatureF);
*/
Serial.println(); //extra spaces to make debugging data easier to read
Serial.println();
if(abs(currentError[b]) > 10) //if output error is large enough, adjust output
{
outputValue[b] = outputValue[b] + currentError[b] / 10;
if(outputValue[b] < 1) //output can never go below 0
{
outputValue[b] = 0;
}
if(outputValue[b] > 254) //output can never go above 255
{
outputValue[b] = 255;
}
analogWrite(outputPin[b], outputValue[b]); //write the new output value
}
if(temperatureC[b] > cutofftemperatureC) //stop charging if the battery temperature exceeds the safety threshold
{
outputValue[b] = 0;
Serial.print("Max Temperature Exceeded");
}
/*
if(temperatureF > cutoffTemperatureF) //stop charging if the battery temperature exceeds the safety threshold
{
outputValue[b] = 0;
}
*/
if(batteryVoltage[b] > cutoffVoltage) //stop charging if the battery voltage exceeds the safety threshold
{
outputValue[b] = 0;
Serial.print("Max Voltage Exceeded");
}
if(millis() > cutoffTime) //stop charging if the charge time threshold
{
outputValue[b] = 0;
Serial.print("Max Charge Time Exceeded");
}
delay(10000); //delay 10 seconds for before next iteration
}
Serial.println();
Serial.print(chargeStatus());
Serial.print(" Out of ");
Serial.print(nBatteries);
Serial.print(" batteries fully charged");
}
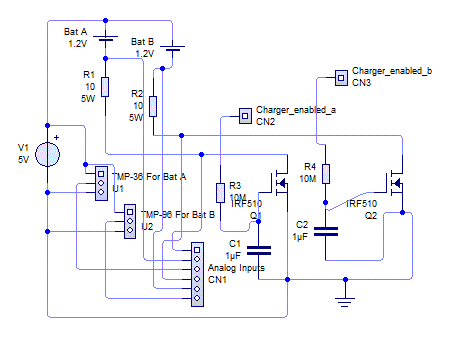
Also, I am not sure if the MOSFET has to be special but it controls the charging voltage according to the All About Circuits page so I will use a IRF510 MOSFET from eBay.

 Circuit Simulator
Circuit Simulator